PROKARYOTES
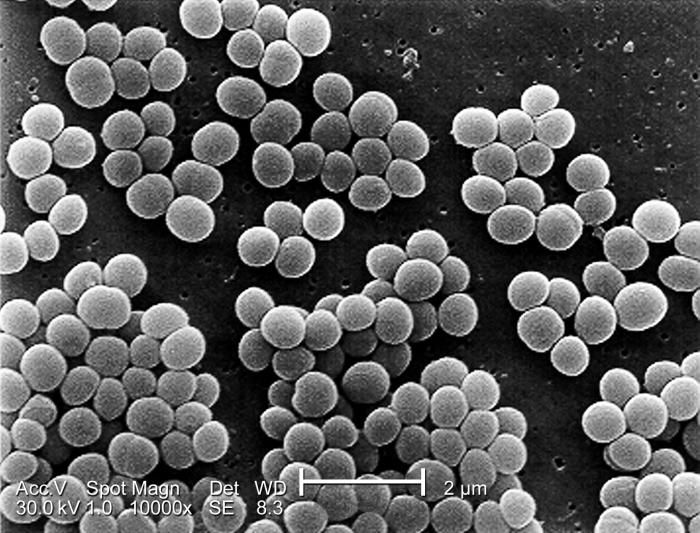
Gram Positive Bacteria
[Public Domain]
Chapter Outline
- Description of Prokaryotes
- Classification of Prokaryotes
- Bacteria
- Cyanobacteria
- Proteobacteria
- Gram Positive Bacteria
- Archaea
Links to external sites will appear in pop-up windows.
GRAM-POSITIVE BACTERIA
The Gram-Positive bacteria are represented by the phyla Actinobacteria and Firmicutes. They are most common in soil and sediment. The difference between the two phyla is based on the levels of guanine + cytosine (G+C) in the organisms. The Actinobacteria have high levels of G+C while the Firmicutes have low levels.
Resources:
|
| ACTINOBACTERIA | |
"These are primarily soil organisms, but some are pathogens or opportunistic pathogens. All are aerobic heterotrophs." (Brown, 2002)
Resources:
|
| FIRMICUTES | |
In the Firmicutes, endospore formation is common. These spores form in response to poor environmental conditions. The cell goes dormant until conditions are better, and examples have been found in fossil amber and halite millions of years old. These spores were revived when subjected to the right environment.
Resources:
|
| [ Previous Page ] | [ Next Page ] |